Let's Understand Different Types of Breaks in Car 2023
Step into the captivating realm of car brakes – the intricate mechanism that ensures you maintain absolute control over your vehicle. These essential components may appear simple on the surface, but beneath that exterior lies a vast domain of engineering innovation and awe-inspiring technology.
Picture your car brakes as a loyal entourage of bodyguards, always poised to spring into action whenever the need arises. What adds to the fascination is the existence of not just one, but several types of brakes. From the robust mechanical brakes reminiscent of the past to the hydraulic powerhouses found in contemporary vehicles, each variety boasts a distinctive approach to enhancing the safety and smoothness of your ride.
Let’s delve into the intricacies of these car brake systems. By the end of this exploration, you’ll possess fundamental knowledge to make informed decisions regarding your vehicle’s safety and performance. Fasten your seatbelt – this journey promises to be secure, steady, and filled with excitement!
How a Tyre Brake Works?

When you press the brake pedal with your foot it keeps all the braking going
This pedal is connected to the master cylinder, which is the main heart of the braking system

The hydraulic master cylinder transforms the mechanical force applied to your brake pedal into hydraulic pressure.
The master cylinder’s piston is pushed when the pedal is depressed, increasing the hydraulic pressure in the brake lines.

In Order to generate hydraulic pressure these strong veins used by master cylinder.
They transfer this pressure to each wheel’s own wheel cylinder or brake calliper.
To provide effective stopping, these brake lines are designed to endure high pressures.

Whether your car has wheel cylinders or brake calipers will depend on whether it has drum or disc brakes.
These parts change mechanical force back into hydraulic pressure.
Wheel cylinders press the brake shoes up against the drums, while brake calipers deliver force to the brake pads.

When the brake pads or shoes make contact with the rotating drums or rotors, the brakes activate.
These parts have a unique friction material lining them, which provides the grip the car needs to slow down or stop.
Resistance is produced when the brake shoes or pads press down on the rotating drums or rotors.
Your car will eventually slow down as a result of this resistance, which transforms the kinetic energy of your motion into heat energy.
Check out Tips to Maintain your Car Batteries.
Different Types of Brake Systems in a Car
After learning about the workings of automobile brakes, let’s investigate the various brake systems that are installed in cars. Every system has its own advantages, from the simplicity of drum brakes to the efficiency of disc brakes.
Let’s examine the various brake system types in more detail:
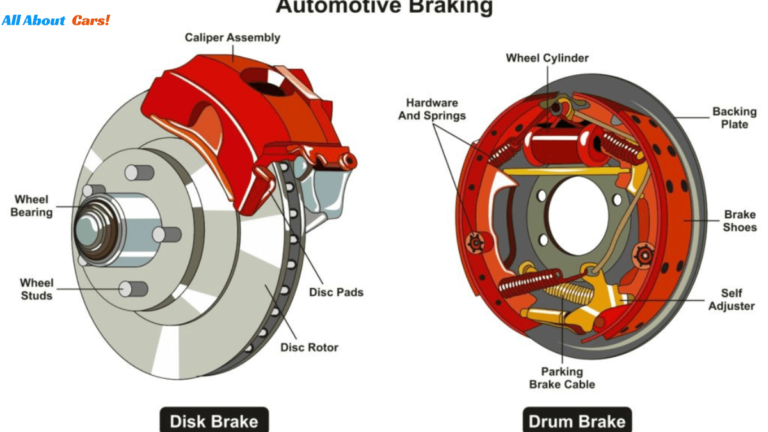
1. Drum Brakes
Drum brakes represent an older-style braking system often located in the rear wheels of certain cars. This system comprises brake shoes, curved metal pads lined with friction material, and a drum—a circular metal surface. Upon pressing the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure causes the brake shoes to expand against the inside of the drum, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle. Drum brakes, characterized by their cost-effectiveness and simple design, are suitable for specific vehicles and driving conditions. However, they may be less efficient at dissipating heat compared to disc brakes, potentially resulting in decreased braking performance during prolonged heavy use.
2. Disc Brakes
On the other hand, disc brakes, the prevailing braking system in modern cars, consist of brake pads, calipers, and a disc rotor attached to the wheel hub. When the brakes are engaged, hydraulic pressure compels the brake pads to squeeze against both sides of the disc rotor, generating friction and decelerating the vehicle.Drum brakes, in contrast to disc brakes, lack the superior performance, efficient heat dissipation, and heightened stopping power that the latter provides. They are also more responsive and provide consistent braking performance, especially during heavy braking. Two types of disc brakes exist: floating caliper disc brakes, where calipers slide on mounting pins, and fixed caliper disc brakes, where calipers are securely mounted in place. Regular inspection and maintenance of disc brakes are crucial to ensure their proper functioning and longevity.
3. Carbon Ceramic Breaks

These high-performance braking systems are commonly found in luxury cars and sports vehicles.
They have discs composed of a ceramic and carbon fiber combination.
Carbon-ceramic brakes provide the benefits of lighter weight, better heat resistance, and longer lifespan.
These brakes are perfect for applications requiring exceptional performance.
Check out Tips to Maintain your Car for long.
How to Choose Perfect Brakes for your Car
The process of selecting the optimal brake system for a vehicle necessitates a thorough examination of several crucial factors. To make a well-informed decision, take into account the following elements:
Vehicle Type
The choice of a brake system should be in harmony with the characteristics of the vehicle. Smaller automobiles often incorporate a aggregate of disc brakes within the front and drum brakes inside the rear, even as larger automobiles may additionally rent disc brakes on all wheels to meet increased demands.
Driving Conditions
Tailor your brake system selection to the environment where you typically drive. For those navigating hills or mountains, a robust braking system is essential to manage the added stress and heat generated during descents.
Brake Pad Material
Different brake pad materials are designed for specific driving conditions. Ceramic brake pads have gained a recognition for their ability to generate minimal noise and convey little or no dirt, making them an top notch choice for city riding.
In contrast, semi-metallic pads offer superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-performance applications or handling heavy loads.
Maintenance Considerations
Assess your willingness to engage in brake system maintenance. Disc brakes, on the other hand, are generally simpler to inspect and maintain when compared to drum brakes.
What are the Features of Brakes in Modern Cars?
Contemporary automobiles are furnished with state-of-the-art braking systems that integrate an array of functionalities designed to augment safety and efficiency. Let’s examine a few of these characteristics in more detail:
1. Anti-Locking Braking System (ABS)
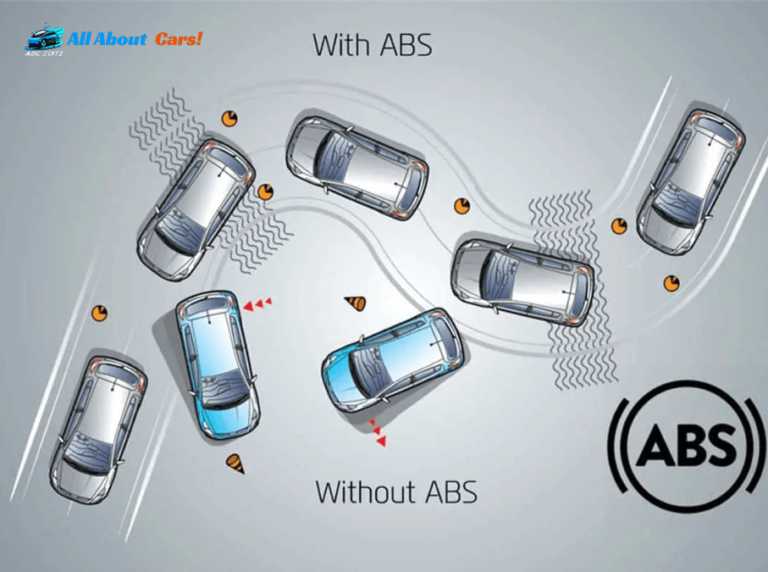
The foundation of automotive safety is ABS, which guarantees that your vehicle maintains control even when using emergency brakes.
It works by employing sensors to identify wheel locking and quickly applying the brakes to stop it.
By doing this, ABS helps you to keep control of your steering, lowering the chance of skidding and obtaining the lowest stopping distance
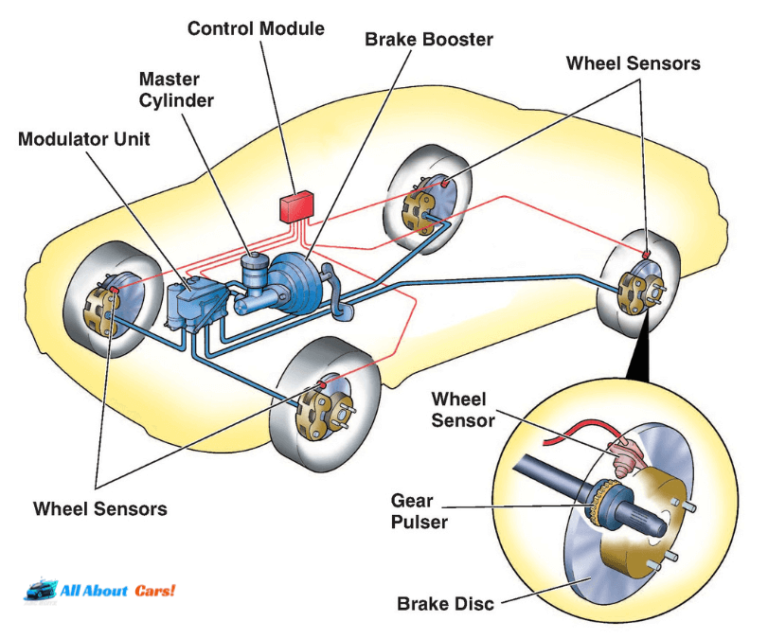
EBD serves as the intelligence behind your car’s capacity to adjust braking force to individual wheels, taking into account factors such as vehicle load and road conditions. This system guarantees that each wheel receives the appropriate amount of braking force, leading to uniform and effective braking. EBD proves particularly valuable when your vehicle is unevenly loaded, preventing wheel lockup and enhancing overall stability.
3. Traction Control System (TCS)
TCS acts as a safeguard against wheel spin, intervening during both acceleration and braking by modifying engine power upon detecting wheel spin, thereby averting skidding. TCS guarantees ultimate tire grip, a crucial factor for maintaining manipulate in unfavourable climate conditions or while navigating slippery terrain.
ESC is an advanced system capable of autonomously applying brakes to specific wheels to counteract skidding or loss of control. This technology enhances your confidence while driving, especially on slippery or challenging road surfaces.
5. Brake Assist
Brake Assist identifies abrupt and forceful pedal applications, augmenting the force you apply to ensure a faster response and a reduced stopping distance. This feature acts as your safety net in unforeseen situations, delivering additional brake force precisely when you need it most.
Check Out Tips to Maintain your 2nd Hand Car.
Types of Tyre Brakes Based on Usage
Let’s explore the intricate realm of tire brakes, categorized based on their specific applications:
Service Brakes
These constitute the primary set of brakes that drivers depend on to slow down or bring their vehicle to a stop. Both disc brakes and drum brakes, as discussed earlier, fall under this category. The choice between these two depends on factors such as vehicle type and intended use.
Mechanical Brakes
Relying on a direct physical connection between the brake pedal and braking components, these brakes activate a mechanical linkage, engaging the brake drums or discs. Although less common in modern vehicles, they find use in classic cars and specialized applications, providing reliable stopping power with simple mechanics. Maintenance and adjustment are crucial to their performance, but they are gradually yielding to more advanced brake technologies in contemporary automobiles.
Parking Brakes (Handbrakes)
Designed to keep the vehicle stationary when parked, these brakes, also known as hand brakes or emergency brakes, can be either mechanical or electronic. They ensure the vehicle remains in place when parked on an incline and typically act on the rear wheels, separate from the primary service brakes.
Regenerative Brakes
A hallmark of hybrid and electric vehicles, regenerative brakes convert a portion of the kinetic energy into electrical energy when the driver applies the brakes. This energy is then stored in the vehicle’s batteries, contributing to enhanced energy efficiency.
Engine Braking
Also known as compression release engine braking, this method relies on the engine’s mechanical resistance to slow down the vehicle. Common in large commercial vehicles, it is engaged by restricting the engine’s intake of air or exhaust gases, helping control speed when descending steep grades and reducing wear on traditional brake components.
Hydraulic Brakes
Finding application beyond the primary braking system, hydraulic brakes are used in various aspects of an automobile, including hydraulic power-assisted steering, hydraulic clutch systems, and hydraulic suspension systems. The hydraulic principle, based on the incompressibility of fluids, ensures reliable and consistent force transfer.
Air Brakes
Commonly found in heavy-duty vehicles, air brakes rely on compressed air to transmit force from the brake pedal to the braking components. Renowned for their durability, air brakes offer robust stopping power.
Our Final Verdict
In summary, car brakes stand as your primary line of defense in ensuring road safety, with each type bringing its distinct strengths to the forefront. Whether it’s the swift responsiveness of disc brakes, the cost-effectiveness of drum brakes, or the cutting-edge capabilities of regenerative brakes in electric vehicles, your car’s braking system showcases a marvel of engineering.
Furthermore, modern safety features such as ABS and EBD enhance your control and stability on the road, elevating the safety and enjoyment of driving. With these advancements, your vehicle transforms into a reliable companion, guaranteeing your safety as you navigate the open road.
The next time you engage that brake pedal, recognize that you’re tapping into a realm of technology and innovation diligently working to keep you and your passengers safe. Drive forward with confidence, armed with the knowledge of your car’s remarkable braking system.
FAQs
Q. What falls under the umbrella of braking types?
Braking sorts embody numerous structures and methods applied to slow down or bring a vehicle to a halt, incorporating hydraulic, mechanical, electromagnetic, and regenerative braking, each possessing distinct advantages and applications.
Q. What are the three most prevalent types of brakes?
The three common types of brakes include disc brakes, drum brakes, and regenerative brakes. Each type boasts unique features and applications.
Q. Which type of brakes is the most widespread?
Hydraulic brakes, renowned for their precision and reliability, stand as the most prevalent type of brakes in modern vehicles. They are favored for their efficiency and versatility.
Q. What roles do car brakes fulfill?
Car brakes play a fundamental role in slowing down or stopping a vehicle by converting kinetic energy into heat through friction, thereby ensuring safety and control.
Q. What varieties of brakes exist in automobiles?
Automobiles showcase a diverse array of brake types, including disc brakes, drum brakes, carbon-ceramic brakes, regenerative brakes, vacuum-assisted brakes, and air brakes. Each is designed to fulfill specific functions and cater to different driving conditions and vehicle categories.
